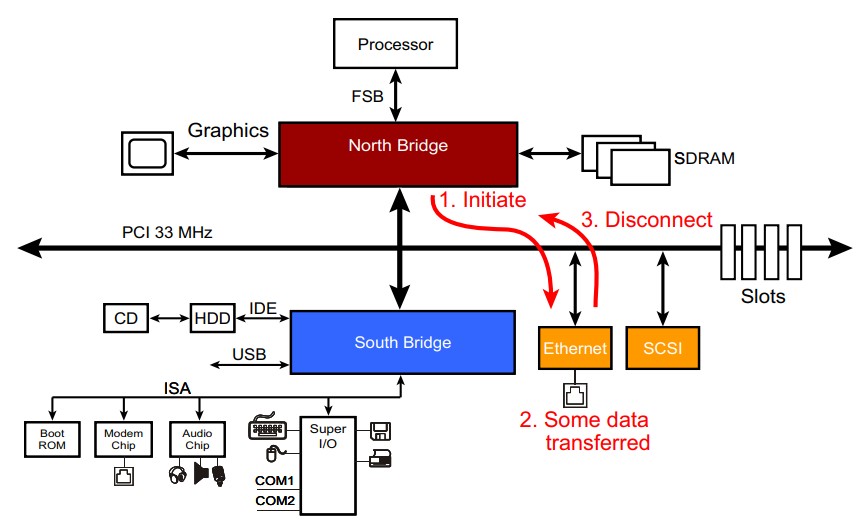
This is similar to PCI Retry Protocol, however in this case part of the data is already transferred and the transaction stops midway and thus disconnected.
Procedure
-
Master initiates a transaction
- Example: North Bridge (master) starts a burst read from the Ethernet device (target).
-
Target claims the cycle and transfers some data
- Unlike Retry, at least one doubleword is transferred successfully.
-
Target can’t continue
- Example: Ethernet device runs out of buffer data.
- It has two choices:
- Insert wait states → if it just needs a few cycles to get more data.
- Disconnect (STOP#) → if it needs more than 8 clocks.
-
How disconnect works
- The target asserts STOP# during the data phase.
- This tells the master: “End this burst now — you got some data, but I can’t continue.”
- The master ends the cycle early, keeping track of the address where it left off.
-
Master after disconnect
- Waits at least 2 clocks.
- Re-arbitrates for the PCI bus.
- When granted, resumes the transaction from the disconnected address (not from the beginning).
-
Bus efficiency
- Disconnect prevents the PCI bus from being tied up with long wait states.
- While the master waits, the arbiter can let other masters use the bus.